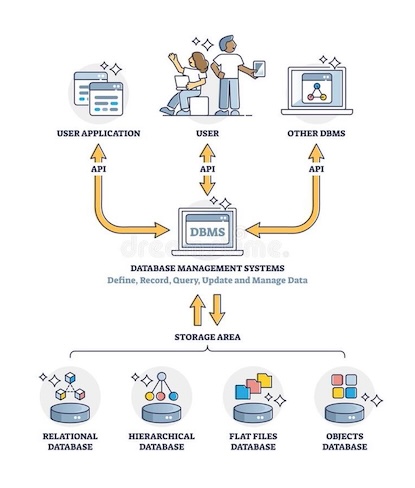
Minisoft ecosystem encompasses the network of organizations, individuals, and resources that interact and influence its operations and success.

Payroll software is a specialized tool designed to automate and streamline the payroll process for businesses of all sizes. It handles critical payroll tasks such as calculating employee wages, taxes, benefits, and deductions with precision, ensuring that employees are paid accurately and on time. The software typically integrates with time-tracking systems, employee records, and accounting software, which helps to eliminate manual data entry and reduces the risk of errors.
For small and medium-sized businesses, payroll software offers significant time and cost savings by automating routine payroll tasks and reducing administrative overhead. It helps ensure that payroll is processed quickly and accurately, without the need for manual intervention or reliance on third-party payroll services. With features like direct deposit, paystub generation, and automatic tax calculations, businesses can improve employee satisfaction by ensuring prompt and accurate payments. Furthermore, payroll software often includes security features to protect sensitive employee data and reduce the risk of fraud. By centralizing payroll data and providing detailed reports, the software helps business owners and HR departments make informed decisions about budgeting, compensation, and tax planning.
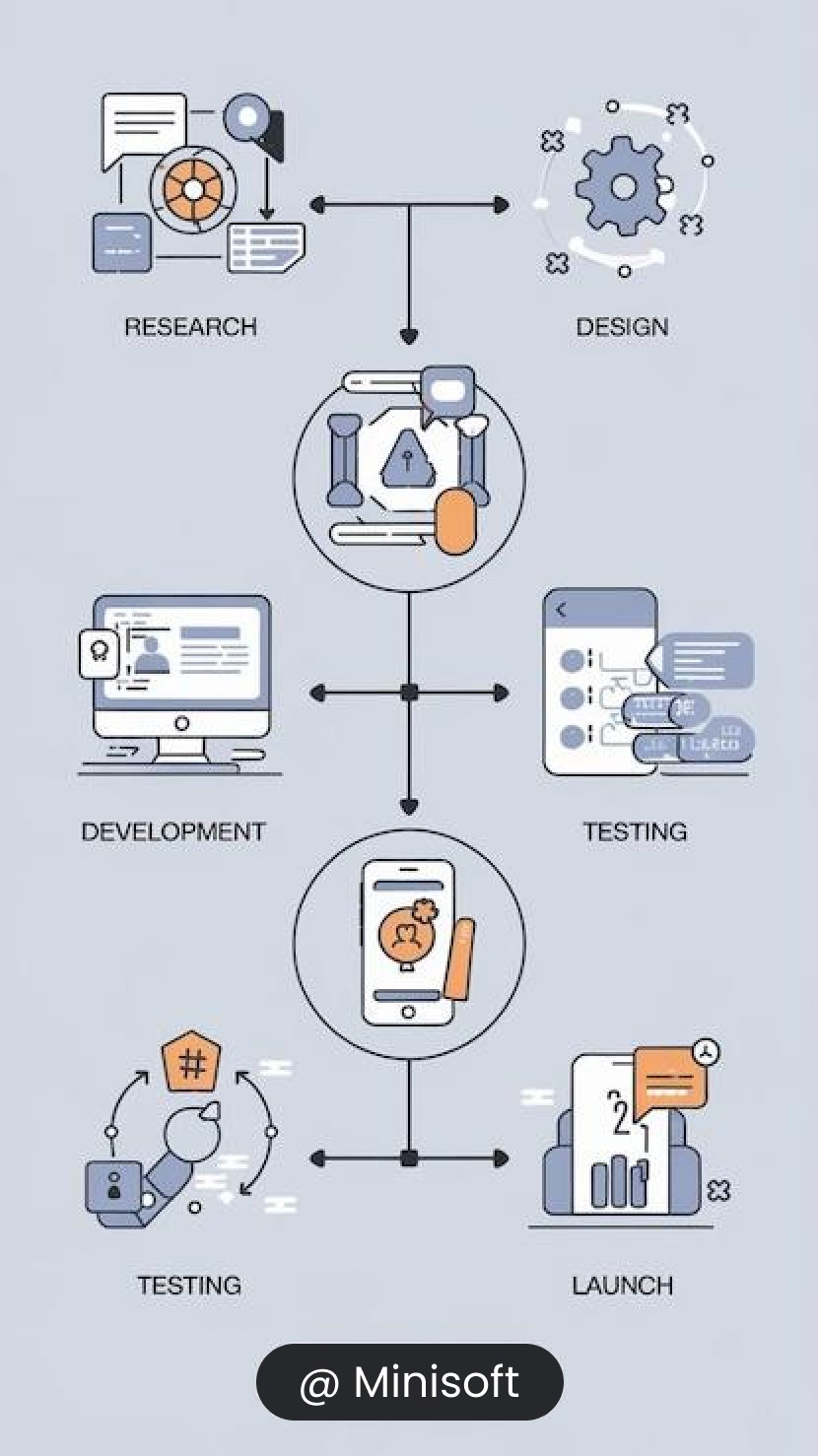
The workflow of payroll software encompasses multiple stages that streamline and automate the payroll process, ensuring accuracy, compliance, and efficiency.
Minisoft ecosystem encompasses the network of organizations, individuals, and resources that interact and influence its operations and success.
Marketing software provides a unified platform for managing all business functions, eliminating silos and inefficiencies. It empowers businesses to optimize their operations, improve productivity, and scale effectively in a competitive market.
Payroll software automates complex calculations for wages, tax deductions, benefits, and bonuses, significantly reducing the risk of human error. It ensures that calculations are accurate every time, minimizing payroll discrepancies and compliance issues.
By automating payroll processes such as calculating hours worked, tax withholdings, deductions, and generating pay stubs, payroll software saves businesses a significant amount of time. This frees up human resources to focus on other strategic tasks rather than manual payroll processing.
Payroll software ensures that all taxes are calculated correctly based on current tax rates and regulations, helping businesses avoid costly tax penalties. It automatically generates tax forms (such as W-2, 1099) and handles tax filings, making compliance easier and more efficient.
Payroll software offers robust security features to protect sensitive employee data. Data is encrypted and stored securely, ensuring that personal information like salary details, tax data, and bank account information are safe from unauthorized access.
Many payroll systems offer employee portals where workers can access pay stubs, tax forms, view their pay history, and request time off. This self-service option empowers employees and reduces administrative tasks for HR, making it easier for everyone involved.
Not using Payroll software in a small-scale industry can lead to several significant drawbacks that impact operational efficiency, growth, and overall competitiveness.